| 1626 All-Stage Differencial PP Amplifier |
I bought 4 cute ST tubes 1626 at the net auction, so I modified 6CL6 all-stage differential push-pull amplifier. Since it is a small ST tube, I could remodel it with minimal modification just by making the hole of the socket larger. Although the output fell considerably, It turned into an amusing and healing and energy saving amplifier while watching it.
 It is 1626 made by RCA. I compare its specification with 6CL6. Although it is small tube, since
it is originally a transmission tube, I expect to be able to withstand the rough usage. The shape
of flat plate reminds me of the output tube UX12A in the reflex type radio which was at home when
I was young. The shape of 1626 is very similar to 12A except that the heater is not direct heat type.
It is 1626 made by RCA. I compare its specification with 6CL6. Although it is small tube, since
it is originally a transmission tube, I expect to be able to withstand the rough usage. The shape
of flat plate reminds me of the output tube UX12A in the reflex type radio which was at home when
I was young. The shape of 1626 is very similar to 12A except that the heater is not direct heat type.1626:
Heater: 12.6 V 0.25 A, Maximum plate voltage: 250 V, Maximum plate current: 25 mA, Maximum plate loss: 5 W
6CL6:
Heater: 6.3 V 0.65 A, Maximum plate voltage: 300 V, Maximum G2 voltage: 300 V, Maximum plate loss: 7.5 W, Maximum G2 loss: 1.7 W, Heater cathode to breakdown voltage: 90 V, G1 Circuit resistance: 500 kΩ for self-bias
If you put the mouse over the image, the image will be enlarged.
(Same below)
 This is the front view of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull amplifier. Since the hole of the
socket can not be changed except by increasing the diameter, the spacing between the tubes is slightly
narrow. Since the tube is not so tall, it is just at the current audio rack. Unnecessary holes in the
chassis are open as it is the second modification.
This is the front view of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull amplifier. Since the hole of the
socket can not be changed except by increasing the diameter, the spacing between the tubes is slightly
narrow. Since the tube is not so tall, it is just at the current audio rack. Unnecessary holes in the
chassis are open as it is the second modification.
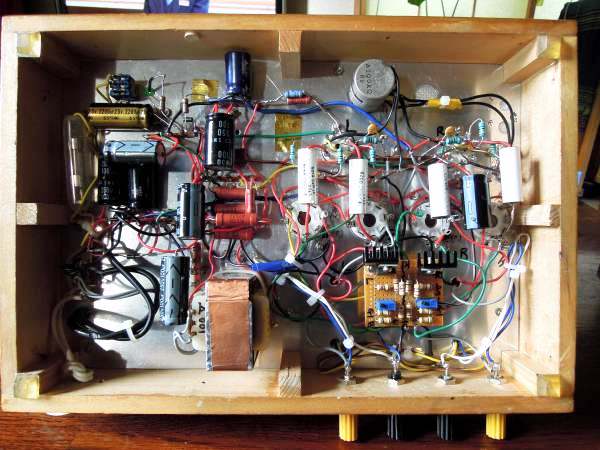 It is the inside view of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull amplifier. The interior is very
dirty as it is the second modification.
It is the inside view of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull amplifier. The interior is very
dirty as it is the second modification.
 This is the circuit diagram of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull amplifier. Basically it is the
same as 6CL6 PP amplifier except that the primary impedance of the output transformer is changed from
16 kΩ p-p to 8 kΩ p-p and the plate current per output tube is reduced from 35 mA to 25 mA.
This is the circuit diagram of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull amplifier. Basically it is the
same as 6CL6 PP amplifier except that the primary impedance of the output transformer is changed from
16 kΩ p-p to 8 kΩ p-p and the plate current per output tube is reduced from 35 mA to 25 mA.
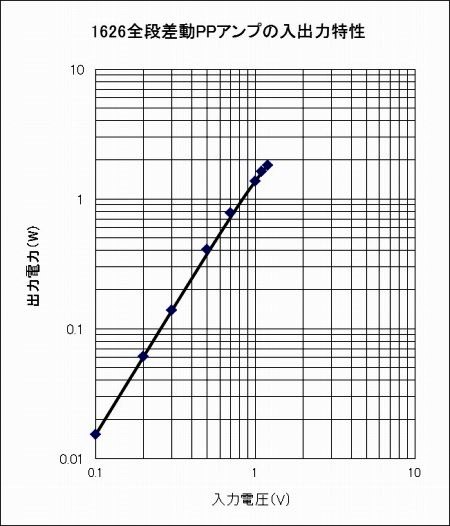 It is the input / output characteristic of the amplifier at 1 kHz. It is almost linear up to about
1 W output, and to about 1.5 W if it accepts distortion. Although the amplifier gain is only 3.5 times,
it always passes preamplifier (gain 2.7 times) so there is no problem. The residual noise is 0.5 mV.
It is the input / output characteristic of the amplifier at 1 kHz. It is almost linear up to about
1 W output, and to about 1.5 W if it accepts distortion. Although the amplifier gain is only 3.5 times,
it always passes preamplifier (gain 2.7 times) so there is no problem. The residual noise is 0.5 mV.
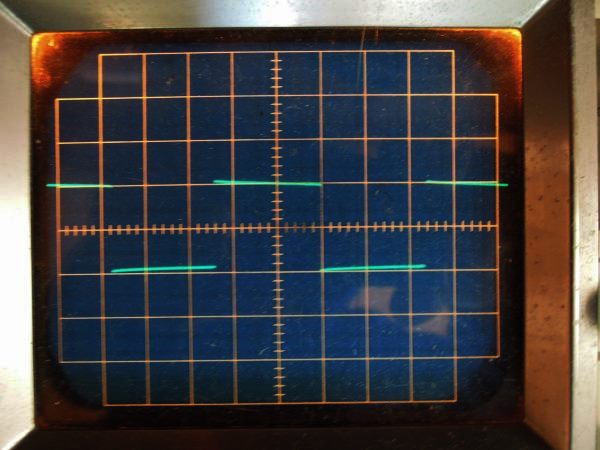 It is square wave response waveform of 100 Hz at 2 V p-p of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull
amplifier. There are a few sags, because the output transformer is so small.
It is square wave response waveform of 100 Hz at 2 V p-p of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull
amplifier. There are a few sags, because the output transformer is so small.
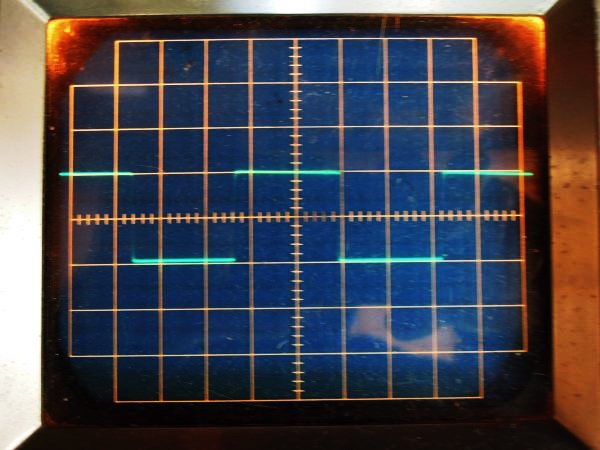 It is square wave response waveform of 1 kHz at 2 V p-p of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull
amplifier. It is straightforward and has no problem.
It is square wave response waveform of 1 kHz at 2 V p-p of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull
amplifier. It is straightforward and has no problem.
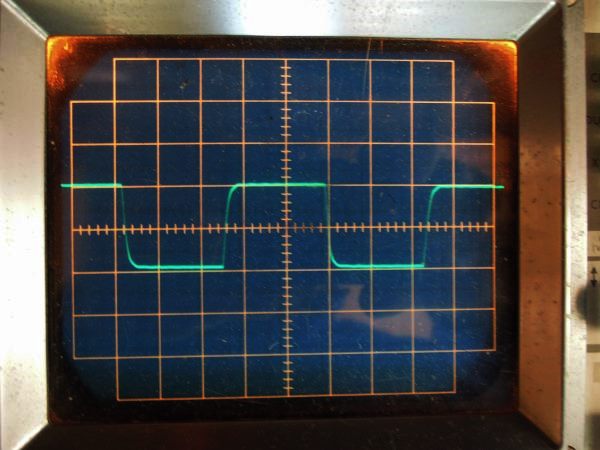 It is square wave response waveform of 10 kHz at 2 V p-p of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull
amplifier. It is a beautiful wave without rampage.
It is square wave response waveform of 10 kHz at 2 V p-p of 1626 all-stage differential push-pull
amplifier. It is a beautiful wave without rampage.
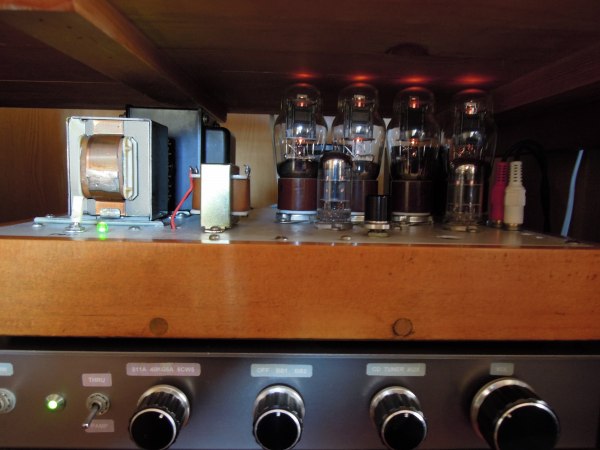 It is 1626 all-stage differential push-pull amplifier housed in the amplifier rack. The height of
1626 seemed to be a problem but it was safe at last. Although it is vacuum tube amplifier under
such a bad condition, generated heat is small and it can be used without worrying even in the
summer. Although it is a push-pull amplifier, only 1.5 W is outputted because of all-stage differential,
but it is enough in my narrow room from bass to treble.
It is 1626 all-stage differential push-pull amplifier housed in the amplifier rack. The height of
1626 seemed to be a problem but it was safe at last. Although it is vacuum tube amplifier under
such a bad condition, generated heat is small and it can be used without worrying even in the
summer. Although it is a push-pull amplifier, only 1.5 W is outputted because of all-stage differential,
but it is enough in my narrow room from bass to treble.
Afterwards Remodeling
Actually, about a year after the completion of this amp, I converted it to the normal push-pull
amplifier (DEPP). The sound of all-stage differential push-pull amplifier was honorable sound
and there was no dissatisfaction, but since I originally liked unique sound, I feel that something
is unsatisfactory. It seems that gorgeous sounds with much distortion rather than the clean sound.
Therefore, the final stage was self-biased by resistance and electrolytic capacitor from the
constant current. I can not believe it, but in my ears with poor frequency characteristic, the
glossy vocal came out towards the front. Although it seems to be scolded by all-stage differential
push-pull amplifier believers, I guess these results came from because 1626 had its own good characteristics as it is originally triode tube.
 It is the final circuit diagram after remodeling. Although the first stage is a differential phase
inversion circuit same as before, but since G1 on one side was dropped to earth, negative feedback
is not applied. The final stage is the self-bias using a single resistance with 2 tubes gathered
together. It is 410 Ω combined with the hand-held resistances, which is almost the same as the
plate current at the all-stage differential. The easiest way to make ordinary push-pull from
all-stage differential is to connect the electrolytic capacitor in parallel to the final stage
constant current circuit, but this time the constant current circuit was also removed. Amplifier
gain, residual noise hardly changed, the maximum output increased to 2.2 W. The newly measured
damping factor value was 1.5.
It is the final circuit diagram after remodeling. Although the first stage is a differential phase
inversion circuit same as before, but since G1 on one side was dropped to earth, negative feedback
is not applied. The final stage is the self-bias using a single resistance with 2 tubes gathered
together. It is 410 Ω combined with the hand-held resistances, which is almost the same as the
plate current at the all-stage differential. The easiest way to make ordinary push-pull from
all-stage differential is to connect the electrolytic capacitor in parallel to the final stage
constant current circuit, but this time the constant current circuit was also removed. Amplifier
gain, residual noise hardly changed, the maximum output increased to 2.2 W. The newly measured
damping factor value was 1.5.
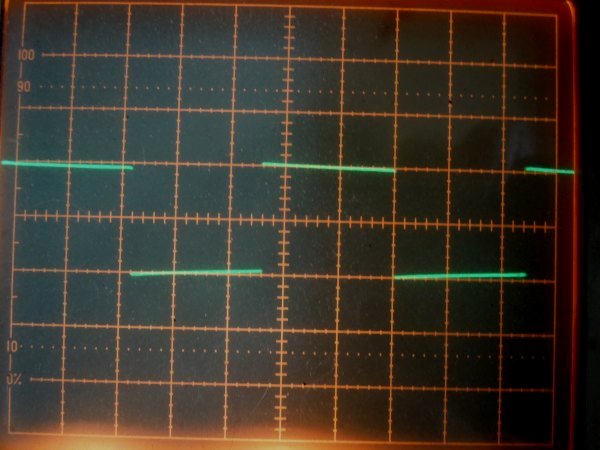 It is square wave response waveform of 100 Hz at 2 V p-p of 1626 push-pull amplifier. Sag is
improved
more than in all-stage differential one, but bass sound is not changed.
It is square wave response waveform of 100 Hz at 2 V p-p of 1626 push-pull amplifier. Sag is
improved
more than in all-stage differential one, but bass sound is not changed.
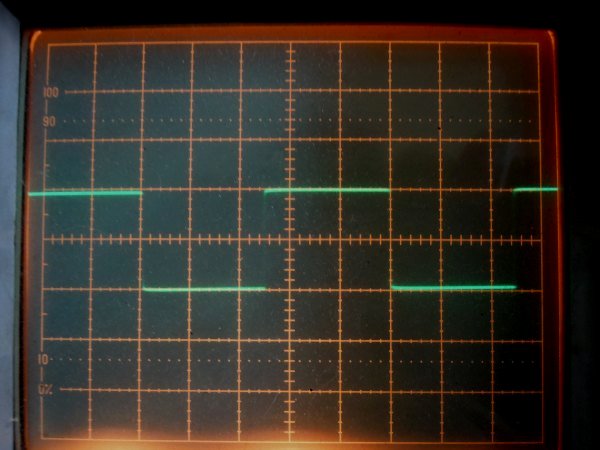 It is square wave response waveform of 1 kHz at 2 V p-p of 1626 push-pull amplifier. It is the
same waveform as in all-stage differential one, but I feel that the vocal sound rather comes
out towards the front.
It is square wave response waveform of 1 kHz at 2 V p-p of 1626 push-pull amplifier. It is the
same waveform as in all-stage differential one, but I feel that the vocal sound rather comes
out towards the front.
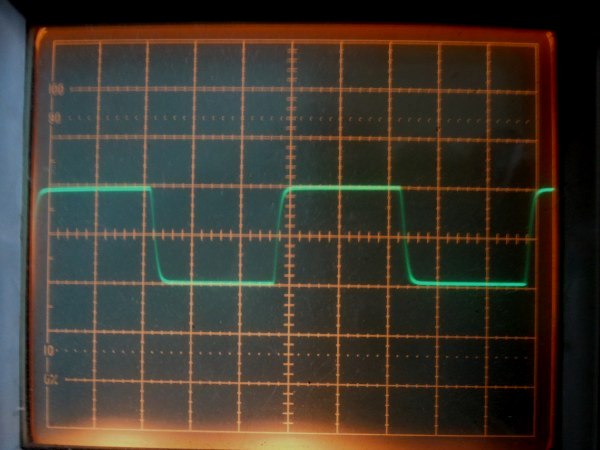 It is square wave response waveform of 10 kHz at 2 V p-p of 1626 push-pull amplifier. The response
is slightly slower than in the case of all-stage differential one.
It is square wave response waveform of 10 kHz at 2 V p-p of 1626 push-pull amplifier. The response
is slightly slower than in the case of all-stage differential one.